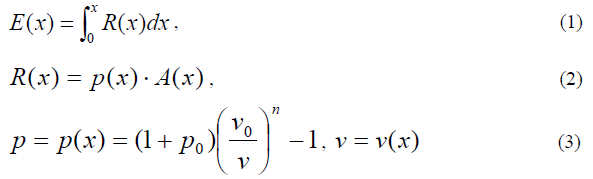Test for Floating Pneumatic Rubber Fenders Based on ISO17357 |
| Author : Date : 2018-03-15 3:28:14 |
Floating pneumatic rubber fender was developed in 1958 based on a rubber company’s technology for rubber aircraft fuel tanks and automobile tires. The progress in the development of such floating pneumatic rubber fenders is closely related to the progress and development in ship technology, and has to continuously cope with larger and larger bulk carriers, oil and gas tankers such as VLCC’s, ULCC’s, large gas carriers and floating structures. Floating pneumatic fenders are used worldwide mostly in ship-to-ship transfer operations, with guidelines provided by OCIMF (Oil companies international marine forum) (OCIMF; 1995, 1997), terminals and by many countries’ navy. These fenders play a critical role in the safe operation of ship berthing. In compliance with the standard ISO 17357, we conducted the prototype test of floating pneumatic rubber fenders such as parallel compression test, angular compression test, durability test, compression-recovery test and puncture-resistance test. We also conducted the test and inspection for commercial fenders, namely, material test, dimension inspection, air leakage test and hydraulic-pressure test, and burst test (endurable pressure test). Performance Test, Parallel Compression Test In the case of pneumatic rubber fenders, the inner air pressure determines properties such as energy absorption and reaction force as per the equations below,
where E, R and p; energy absorption, reaction force and inner air pressure at displacement x, A; contact surface area at x, v; volume of fender, p0 and v0; initial inner air pressure and volume, n; polytropic index. From Eq.2 the reaction force is derived from the inner air pressure multiplied by the contact surface area. The parallel compression test based on ISO17357 is carried out for a prototype fender, 1000mm diameter x 2000mm length (Pneumatic 50) using a 10,000kN compression test apparatus. The compression test is conducted twice with a 5 min. interval. The deflection, reaction force and inner air pressure (which is equal to the hull pressure) are measured as time series data. The ambient temperature is 33.2-Celsius degree and the compression speed is 77mm/min. |

 info@dolphinmarines.com
info@dolphinmarines.com